In our hyperconnected world, a hidden chemical in the brain is quietly shaping how we interact with technology: dopamine. Often dubbed the brain’s “reward molecule,” dopamine drives our motivation, reinforces habits, and can create powerful feedback loops with digital devices. Understanding digital dopamine is key to breaking free from tech addiction and reclaiming mental clarity.
What is Dopamine? A Simple Neuroscience Primer
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in motivation, reward, and learning. Neuroscience describes dopamine’s functions as:
- Wanting: The urge or motivation to seek rewards
- Liking: The pleasurable response upon receiving rewards
- Learning: Associating behaviors with outcomes through feedback
These functions involve brain regions such as the ventral tegmental area, nucleus accumbens, and the prefrontal cortex—the latter governing decision-making and impulse control .
Digital Dopamine: How Technology Hijacks Your Brain
Digital devices exploit dopamine’s “wanting” system. Social media platforms simulate variable reward schedules, delivering unpredictable likes and notifications—creating potent dopamine bursts that fuel compulsive “dopamine-scrolling.” Smartphones act like constant dopamine delivery devices, conditioning craving similar to substance addiction.
Research from the National Institutes of Health confirms that digital technology overstimulates dopamine pathways similarly to drug addiction, disrupting cognitive control and emotional regulation—particularly in teenagers .
Dopamine-Scrolling and Dopamine Fasting
Dopamine-Scrolling: The Modern Digital Habit
Dopamine-scrolling is the compulsive act of endlessly scrolling through digital content, driven by small, unpredictable bursts of dopamine in the brain’s reward system. Unlike doomscrolling, which focuses on negative content, dopamine-scrolling is the pursuit of entertaining, novel content that continuously hooks users through the brain’s reinforcement mechanisms .
This pattern exploits variable reward schedules, making each scroll potentially rewarding and reinforcing the habit. Billions are engaged in dopamine-scrolling daily, leading to mental distraction and decreased wellbeing.
Dopamine Fasting: Resetting Your Brain’s Reward System
Dopamine fasting is a wellness technique involving scheduled breaks from dopamine-triggering activities like social media and gaming to help reset dopamine sensitivity. Dopamine boosts by social media and gaming addiction are quite similar to those experienced by recreational drug users. While research on dopamine fasting is still evolving, studies on dopamine receptor plasticity induced by recreational drugs suggest these breaks can improve emotional regulation and reduce addictive cravings when combined with mindful tech use .
Neurological Impact of Digital Dopamine Addiction
Prolonged dopamine overstimulation affects brain structure and function:
- Decreased prefrontal cortex activity weakens impulse control and prioritization .
- Dopamine receptor desensitization reduces reward sensitivity, causing tolerance .
- Neuroplasticity adapts to favor immediate gratification, undermining long-term goals.
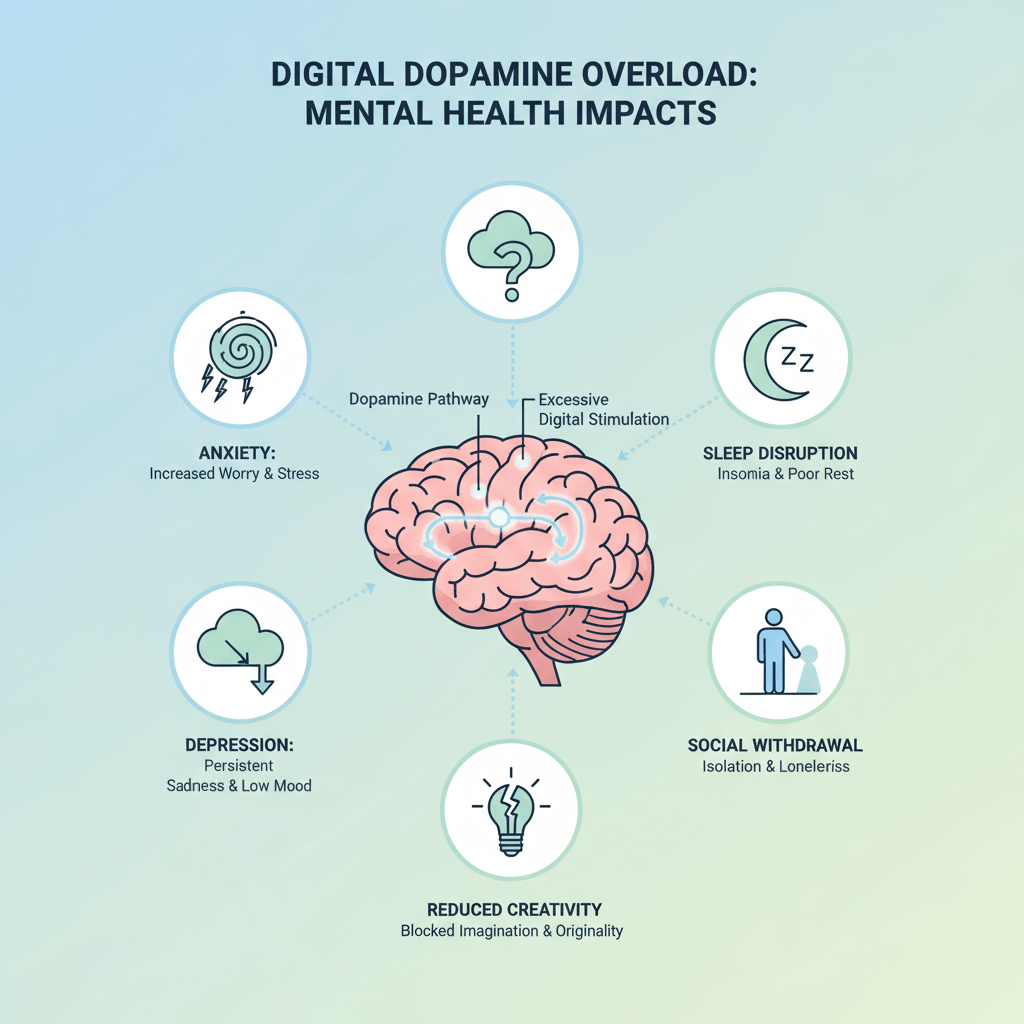
Mental Health Consequences
Excessive digital dopamine stimulation from frequent use of smartphones and social media is linked to increased anxiety and depression. Overactivation of dopamine pathways disrupts emotional regulation and heightens stress sensitivity, especially in young people.
Screen overuse also causes sleep disturbances due to blue light exposure and constant mental stimulation. Poor sleep further worsens mood disorders and impairs cognitive function .
Dopamine-driven tech habits fragment attention and reduce creativity. Rapid content switching makes sustained focus difficult, impacting productivity and memory .
Social withdrawal is common, as digital interactions replace face-to-face connections. This can increase feelings of loneliness and reduce vital emotional support .
Overall, these effects form a vicious cycle where dopamine cravings drive excessive digital use, worsening mental health and social isolation.
The Science of Dopamine Reward Pathways in Digital Addiction
Understanding how dopamine circuits influence behavior helps explain why digital technology is so compelling and hard to resist. The brain’s reward system functions on prediction error signals, where unexpected rewards trigger larger dopamine bursts, making smartphones and social media highly addictive by constantly offering unpredictable stimuli.
This neuroscience insight informs why apps use push notifications, variable content feeds, and gamification to maximize engagement .
Dopamine’s Role in Attention and Focus — Why Screens Fragment the Mind
Digital dopamine impacts the brain’s attention networks, especially the prefrontal cortex, making sustained focus difficult. Frequent dopamine spikes cause rapid shifts in attention, impairing working memory and task persistence.
This neurological effect explains why multitasking with digital devices reduces productivity and why digital overuse is linked to increased ADHD-like symptoms in some populations .
Emerging Technology and Ethical Challenges Around Digital Dopamine
Tech companies increasingly face scrutiny over deliberately designing products that exploit dopamine-driven behaviors. Ethical design frameworks advocate for “time well spent” paradigms prioritizing user wellbeing over engagement metrics.
Public health discussions now call for regulation of dopamine-driven features, transparency in algorithmic feeds, and options to customize reward exposures to reduce addictive potential .
Practical Strategies to Balance Digital Dopamine
Beyond detox and dopamine fasting, practical day-to-day actions can mitigate dopamine overstimulation:
- Setting app usage limits with built-in phone tools
- Turning off non-essential notifications
- Using grayscale mode to make phones less enticing
- Scheduling offline activities and social interactions
- Practicing mindfulness and meditation to improve impulse control
Combining these habits leads to sustainable digital wellbeing and improved dopamine system balance .
The Future of Digital Dopamine Research and Tech Design
Advances in neuroscience and ethical tech design continue to emerge, focusing on developing apps and platforms that encourage balanced dopamine signaling. Artificial intelligence in personalization may shift toward supporting healthier digital behaviors, making the future of technology less addictive and more user-centered .
Conclusion
Digital dopamine fundamentally shapes how technology captivates our brains—offering both motivation and potential peril. With deep neuroscience understanding and mindful strategies, individuals can reclaim control over their digital habits, protecting mental health and productivity in the evolving digital landscape.
For those looking to actively manage and balance their digital dopamine levels, a structured digital detox can be a highly effective step. Taking intentional breaks from screens helps reset your brain’s reward system, reduces stress and anxiety, improves sleep quality, and enhances your focus and overall mental health. To explore practical strategies and evidence-based benefits of a digital detox, check out our in-depth guide on How to Do a Digital Detox at Home and start reclaiming control over your digital habits today.
FAQS
Can dopamine-scrolling lead to actual brain changes similar to drug addiction?
Many wonder if dopamine-scrolling—the compulsive social media scrolling—is just a bad habit or if it causes real neurological changes like substances do. Research shows that while the pattern exploits brain reward pathways similarly to drugs, the exact long-term brain impact is still under study and differs by individual.
Is dopamine fasting scientifically proven, or is it just a wellness fad?
Dopamine fasting is popular but controversial. Scientific studies support the brain’s capacity for receptor plasticity and recovery during abstinence but dopamine fasting as popularly described lacks extensive rigorous evidence. It can be useful combined with broader mindful habits .
How quickly can the brain recover dopamine sensitivity after reducing digital overstimulation?
The timeframe varies widely. Some receptor and behavioral changes can begin within days or weeks of abstinence, but full normalization may take months depending on addiction severity and individual neurobiology .
Why do people often feel bored or anxious when they try to reduce digital dopamine stimulation?
This is a form of withdrawal where the brain’s reward system seeks dopamine hits it was accustomed to. The discomfort reflects neurochemical imbalance and usually fades with sustained behavioral changes and alternative natural rewards .
Can digital dopamine addictive behaviors affect children and teenagers differently?
Yes, younger brains are more plastic and sensitive to dopamine signals. Overexposure during critical developmental periods may increase vulnerability to compulsive digital behaviors and mental health issues, necessitating careful digital use guidance .












