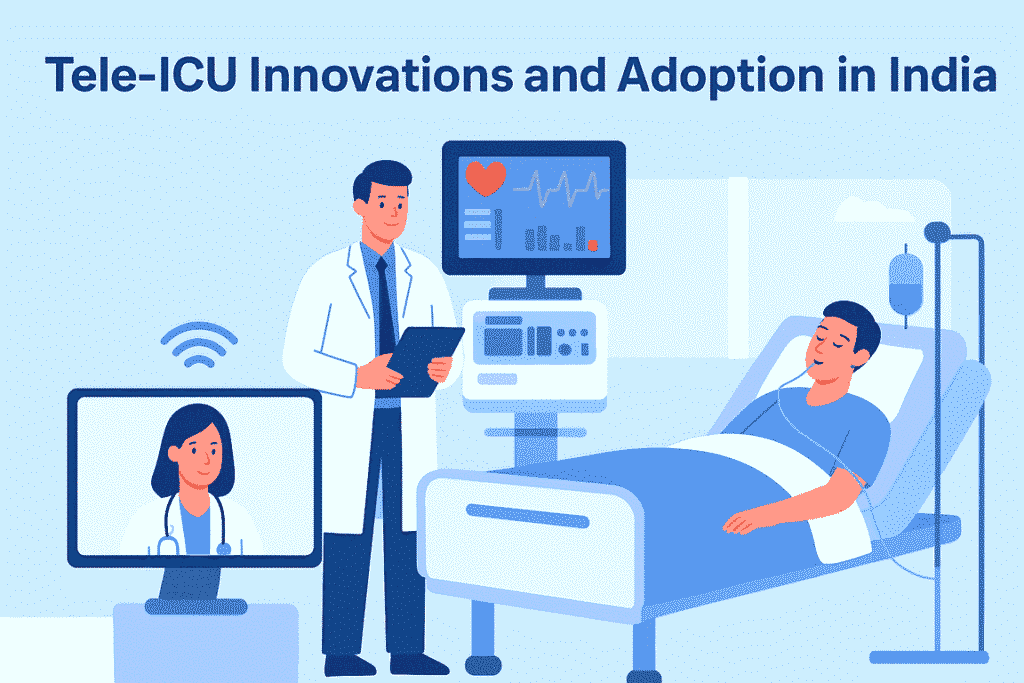
India’s healthcare system is undergoing a transformation as it responds to a growing population, a rising chronic disease burden, and an uneven distribution of healthcare resources. In this context, tele-intensive care units (Tele-ICUs) are emerging as a game changer. Using telecommunications and advanced monitoring technologies, Tele-ICUs allow specialists to remotely oversee critically ill patients—bridging gaps in access to quality intensive care, particularly in tier 2 and tier 3 cities, and lowering overall treatment costs.
Tele-ICU Market Growth in India
The Indian Tele-ICU market has grown significantly over the past few years. From a modest valuation of $32 million in 2019, it is projected to exceed $169 million by 2027, representing an impressive CAGR of nearly 24% (according to Research and Markets).
Driving factors include government-backed digital health initiatives, a surge in ICU admissions, wider adoption of cloud-based platforms, and an increasing focus on healthcare equity.
On the global stage, the Tele-ICU market is already valued at $4.26 billion in 2024 and is forecast to hit $20 billion by 2035, with a CAGR above 15% (GlobeNewswire).
What is Tele-ICU?
Tele-ICU integrates a network of critical care specialists, video conferencing tools, wearable sensors, AI-powered predictive analytics, and electronic health records (EHR) into a central system. This allows intensivists to:
- Monitor patient vitals remotely in real time.
- Detect early signs of deterioration using AI-driven alerts.
- Guide on-site teams with decision support, even if they are not physically present.
This model is particularly relevant in India, where intensivists are concentrated in urban hubs and smaller hospitals often struggle to maintain 24/7 ICU coverage.
Key Innovations Powering Tele-ICU
- AI and Predictive Analytics: Machine learning algorithms predict patient deterioration early by analyzing vital trends and lab results.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Allow for scalable, multi-hospital monitoring systems at lower costs.
- IoT and Wearable Sensors: Enable continuous patient monitoring, even in rural ICUs.
- Mobile Penetration: With India’s high-speed internet access, real-time consultations and alerts are possible across remote geographies.
- EMR Integration: Ensures smooth workflows and accurate documentation across facilities.
Indian Leaders in Tele-ICU
Several Indian hospitals and startups are spearheading adoption:
- Medanta’s e-ICU Command Center – In 2023, Medanta partnered with GE Healthcare to establish a centralized Tele-ICU hub, the first large-scale facility of its kind in India (MetaTech Insights).
- Apollo TeleHealth Services – Runs Tele-ICU programs that combine remote monitoring with on-ground specialist visits, expanding reach into tier 2 and 3 cities.
- Aster DM Healthcare – Uses a hub-and-spoke Tele-ICU model, remotely monitoring hundreds of patients in underserved regions.
- Tricog Health – A Bangalore-based MedTech company offering AI-powered remote cardiac diagnostics, including cloud-based ECG and echocardiogram analysis. Their InstaECG and InstaEcho platforms empower clinicians in remote regions to send patient data to centralized expert teams for real-time interpretation.
- Narayana Health – Known for efficiency-focused innovations, it is experimenting with hybrid remote ICU models.
- HealthNet Global + Tata Tele Services – Collaborating on 24/7 Tele-ICU pilot programs in semi-urban hospitals.
Global Players Shaping the Indian Market
- GE Healthcare Command Center – Combining AI and ICU oversight, GE has partnered with Indian hospitals.
- Hicuity health – US-based providers influencing care models in emerging markets.
- InTouch Health – Provides modular telemedicine solutions providing virtual stroke care.
Benefits of Tele-ICU in India
- Expands access to specialist intensivists beyond metro hubs.
- Reduces mortality and complications via continuous monitoring.
- Helps hospitals lower ICU costs by preventing avoidable transfers and complications.
- Strengthens rural healthcare delivery.
- Optimizes ICU bed utilization by improving triage and monitoring.
Challenges to Wider Adoption
- Digital infrastructure gaps in rural areas.
- Integration issues with different EMR systems.
- Need for workforce training to collaborate with remote intensivists.
- Regulatory and data privacy concerns.
- Cost barriers for smaller hospitals to invest in Tele-ICU technology.
Future Outlook
According to Expert Market Research, the focus will increasingly shift toward AI-driven predictive care, wearable integration, and hybrid models where on-site and remote intensivists work together. Public-private partnerships and startup innovation will be critical in making Tele-ICUs affordable and accessible at scale.
India’s Tele-ICU revolution is not just about new technology—it’s a systemic shift toward equitable, cost-efficient, and accessible critical care.